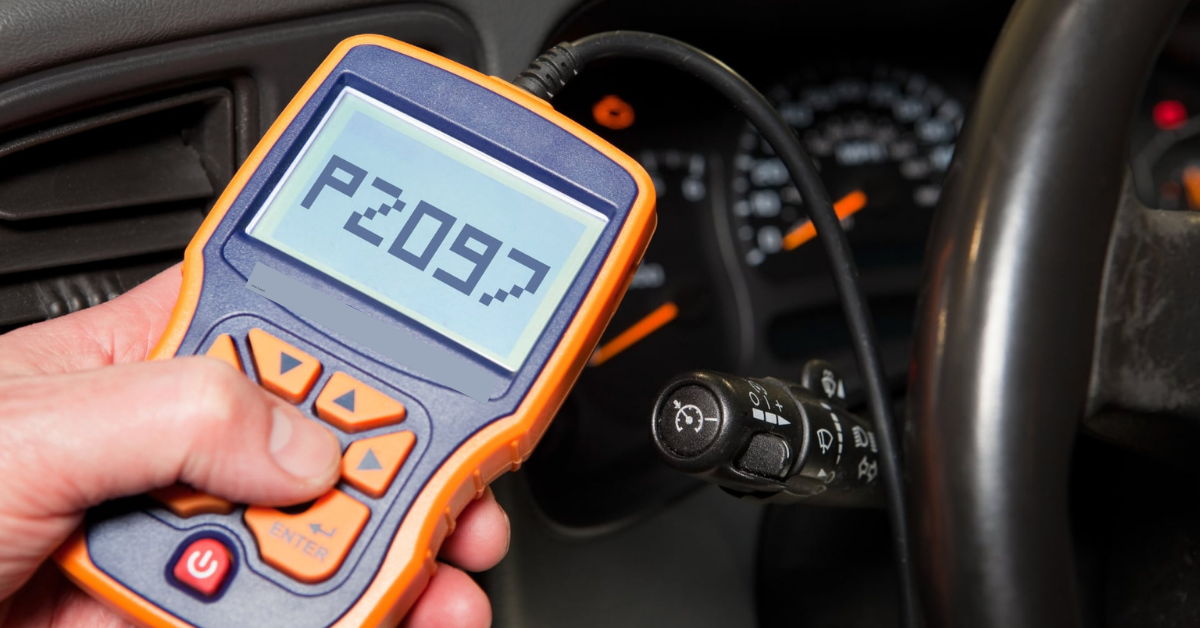
The P2097 code is a diagnostic trouble code that typically appears when there’s an issue with the fuel trim system in Bank 1 after the catalyst. This code is triggered when the oxygen sensor detects an imbalance in the air/fuel ratio, indicating a rich condition. A rich condition means there’s too much fuel in the exhaust stream, which prevents the engine from running smoothly and efficiently.
When this happens, the powertrain control module (PCM) attempts to adjust the ratio to restore balance, but if the issue persists, it can lead to poor engine performance and a reduced fuel economy. Often, the Check Engine Light will be illuminated, alerting you to the problem. The causes can vary, from a faulty oxygen sensor to exhaust leaks, but it’s important to address this issue promptly. If left unchecked, it can lead to more serious engine damage over time.
What Does the P2097 Code Mean?
The P2097 code refers to a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that is triggered when the engine control module (ECM) detects a rich condition in Bank 1, specifically after the catalytic converter. This means that the fuel mixture is too rich, causing the exhaust gases to contain excessive fuel. As a result, the air-fuel mixture isn’t burning as efficiently as it should, potentially leading to engine damage, clogging, and failed emissions tests.
The Check Engine Light is usually illuminated, signaling the issue. The oxygen sensors both downstream and upstream monitor the exhaust and send readings to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). If the sensor registers too much fuel or oxygen in the gases, the fuel trim is adjusted to correct the imbalance.
A rich condition can lead to excessive fuel consumption, and if not addressed, it can eventually damage the engine or its components. The P2097 code may also show up alongside other codes like P0171 (lean condition) or P0172 (rich condition).
What are the Possible Causes of the P2097 Code?
1. Rich Running Condition
A rich running condition can occur when the engine is supplied with too much fuel, leading to a P2097 code. This could be due to faulty components like the oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks, or issues with the fuel system.
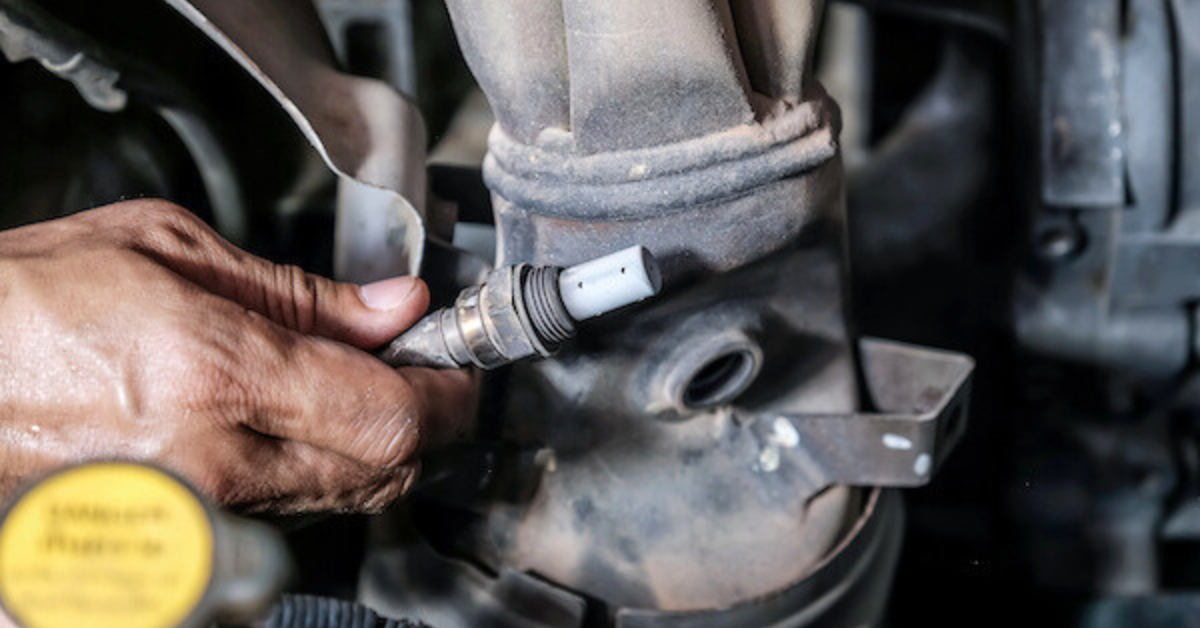
2. Faulty Oxygen Sensor
The oxygen sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. If the sensor is malfunctioning or faulty, it can lead to inaccurate readings, causing the ECM to adjust the fuel mixture incorrectly. This leads to an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture and could trigger the P2097 code.
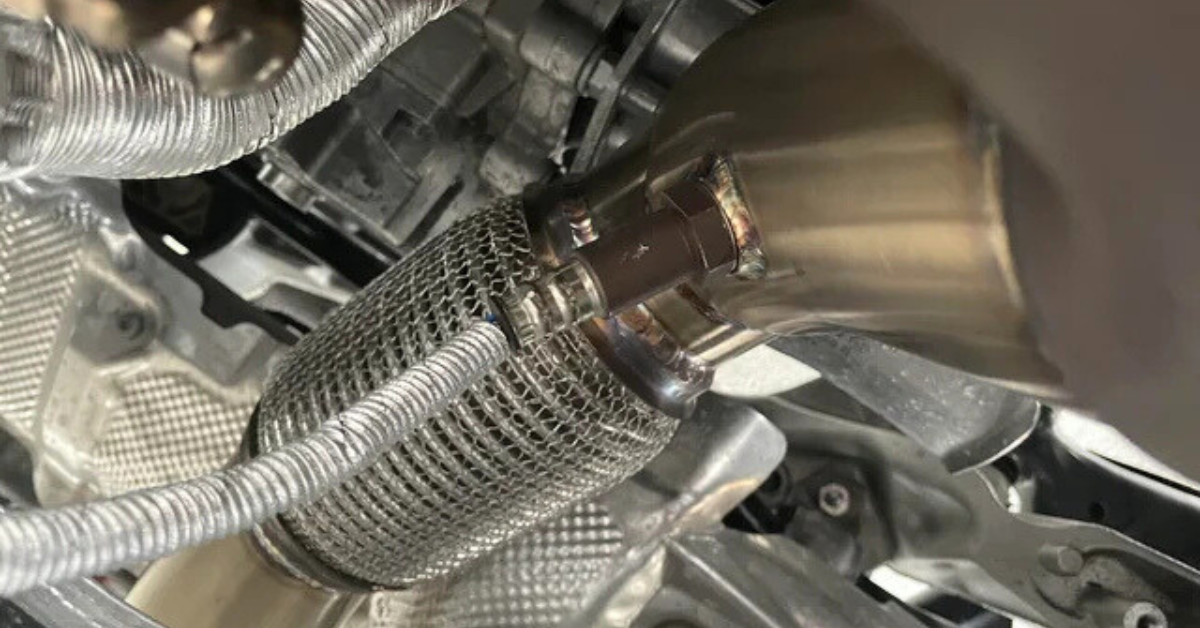
3. Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks can allow unregulated air to enter the exhaust stream, disrupting the readings from the oxygen sensors. This can create an unbalanced mixture, leading to the system mistakenly thinking the fuel is too rich, thus triggering the P2097 code.
4. Damaged Wiring or Poor Connections
If there are damaged wires, poor connections, or moisture in the oxygen sensor circuit, it can cause inaccurate readings. Chaffing, breaks, burns, or damaged pins in the wiring can also disrupt the flow of information from the sensor to the ECM, resulting in improper adjustments to the fuel trim.
5. Malfunctioning PCM
A malfunctioning PCM (Powertrain Control Module) can trigger the P2097 code. In some cases, this could happen due to a software update issue, causing incorrect readings or faulty adjustments in the fuel trim system.
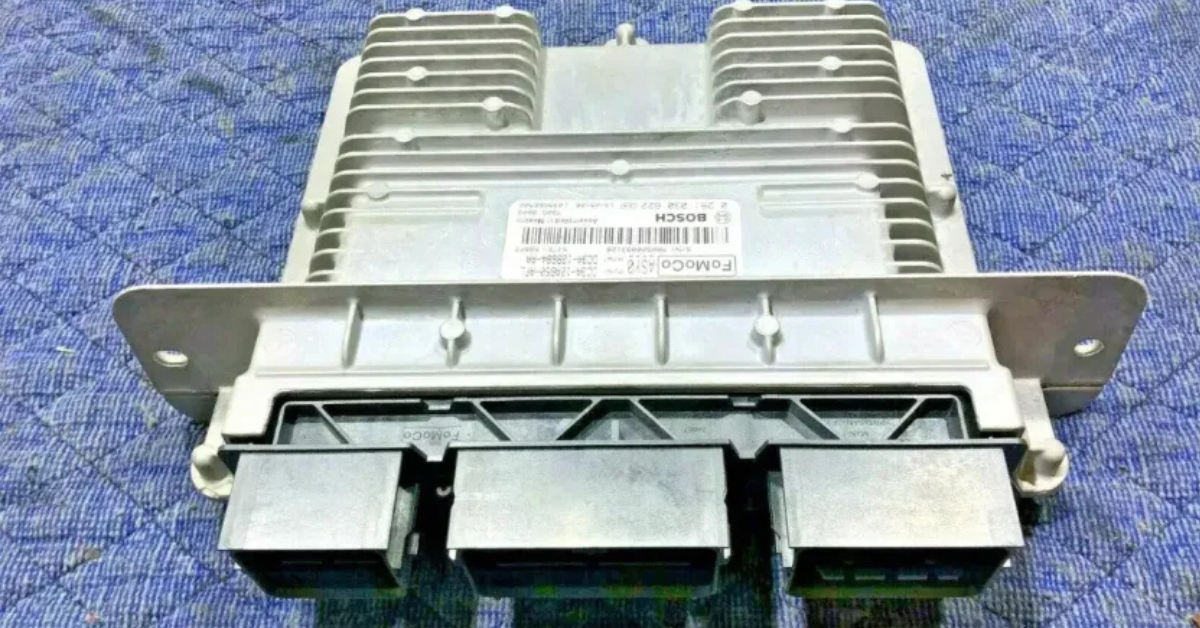

6. Exhaust System Issues
Problems such as exhaust system leaks, a failing catalytic converter, or a broken post-catalyst oxygen sensor can cause the air-fuel mixture to become unbalanced. A contaminated or damaged catalytic converter might allow untreated exhaust gases to pass through, further affecting the oxygen readings and triggering the P2097 code.
7. Fuel System Issues
Other issues related to the fuel system, such as low fuel system pressure, contaminated fuel, or lean fuel injectors, can contribute to a rich condition. Problems in the air induction system, vacuum hoses, or air intake ducts can also interfere with the engine’s air-fuel balance, potentially causing the P2097 code.
8. Aftermarket Parts and Non-OE Components
The use of non-OE oxygen sensors, Aftermarket air filters, or air intake components can cause improper air-fuel adjustments. These parts may not be calibrated for the specific needs of your vehicle, leading to incorrect sensor readings and potentially triggering the P2097 code.
What are the Common Symptoms of the P2097 Code?
- Check Engine Light illuminated
- Poor engine performance
- Reduced fuel economy
- Poor idling or erratic idling
- Rough idling
- Stumble or hesitation during acceleration
- Hard starting when the engine is hot
- Fuel odor in some cases
- Black smoke coming from the tailpipe in extreme cases
- Related DTCs may be registered
- Worse engine performance than usual
- Strong tailpipe odor
- Excessive fuel consumption
Read More:
Honda Code A127: [Checklist, Service Cost & How to Reset]
Error P0011 Code Explained: [ Causes, Symptoms, Fixes and Repair Cost]
How to Diagnose the P2097 Code
Diagnosing the P2097 code can be challenging without proper automotive knowledge, so if you’re not confident with your repair know-how, it’s best to seek expert advice from a mechanic. The process usually starts with a scan test to check for any fault codes. Once you’ve connected a code reader and reviewed the stored codes, active codes, and pending codes, it’s time to erase them and then drive the vehicle to see if the codes return.
If they do, continue your diagnosis by monitoring the oxygen sensor outputs. Focus on upstream Sensor 1 and downstream Sensor 2 on Bank 1 to verify that the sensors are adjusting correctly. If the readings stay constant, even when you adjust the throttle, the O2 sensor or its harness may be bad. In this case, you can test the sensor using a multimeter to check if the readings fall within normal parameters.
You should also inspect the exhaust system for rust holes, poorly-sealed joins, or gasket leaks at the manifold, as these could cause false readings to be sent to the ECM, triggering the P2097 code.
How to Fix the P2097 Code
To fix the P2097 code, start by diagnosing the issue in your vehicle. The repair process may vary depending on the year, make, and model of the car, so make sure to research a solution tailored to your specific vehicle using auto repair resources and guides. If the issue points to a faulty oxygen sensor, you can replace it using basic hand tools and an oxygen sensor socket.
After installing the new sensor, don’t forget to clear the trouble codes. If exhaust leaks are found, inspect the location of the leaks and repair them by replacing gaskets, clamps, or parts of the exhaust pipe. This will help restore the air-fuel balance. For issues with a clogged or damaged catalytic converter, consider cleaning it as a temporary fix or replace it for better long-term reliability.
Understanding the Dynamics of Fuel Trim Adjustments
Fuel trim is a critical system that helps your engine maintain the right balance of air and fuel. Unlike using an oscilloscope or meter, fuel trim data is often gathered via a scan tool connected to the car’s datastream. The short fuel trim represents the immediate response of the ECM or PCM to changes in the oxygen level sensed by the O2 sensor, especially the upstream sensor.
This short-term adjustment is typically kept near zero to maintain the perfect mix of air and fuel. If the mixture becomes too rich, the fuel trim adjusts to the MINUS side. If it becomes too lean, the adjustment moves to the PLUS side. Long fuel trim, also known as its big brother, makes coarse adaptive adjustments when necessary to bring the total fuel trim back into balance.
When you observe the data stream numbers and notice double digits on either side of zero, it may indicate a vacuum leak, a saturated EVAP canister, or an issue with excess HC in the intake during purge. The downstream sensor or rear O2 sensor input plays a role in detecting whether the mixture is too rich or lean, which impacts how the engine adjusts.
Balancing all these elements is a delicate act, and when misbalanced, it can lead to performance issues, signaling the need for diagnostics.

How much does it cost to fix p2097?
If you’ve encountered the P2097 code(Post Catalyst Fuel Trim System Too Rich Bank 1). you’re likely wondering how much it will cost to get your vehicle back in top shape. The cost to fix this issue depends on the underlying cause and can vary depending on your car’s make and model, as well as the repair shop you choose. Here’s a breakdown of typical repair costs:
- Oxygen Sensor Replacement: If the oxygen sensor is faulty, it could cost anywhere between $150 and $300 USD (approximately €130–€260 EUR) to replace the downstream oxygen sensor, which is often the cause of the P2097 code.
- Exhaust Leak Repair: If exhaust leaks are contributing to the problem, repairing them can range from $100 to $400 USD (about €85–€345 EUR), depending on the location of the leak and the complexity of the repair.
- Catalytic Converter Replacement: A damaged catalytic converter may require a more expensive repair, typically ranging from $500 to $2,500 USD (around €430–€2,150 EUR), depending on the severity of the issue and whether the converter needs to be replaced or just cleaned.
- Fuel Injector Cleaning or Replacement: If the fuel injectors are dirty or malfunctioning, the repair cost can range from $200 to $600 USD (approximately €170–€515 EUR).
- Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement: If the mass airflow sensor is contributing to the issue, expect to pay between $150 and $400 USD (about €130–€345 EUR) for a replacement.
On top of the parts, labor costs usually range from $75 to $150 USD per hour (approximately €65–€130 EUR), depending on the complexity of the job and your location.
NOTE: It’s important to remember that these prices can vary based on the vehicle make and model, the labor rates in your area, and the specific parts your vehicle requires. To get a more accurate estimate, it’s recommended that you consult with a certified mechanic or repair shop for an exact quote.
| Repair/Replacement | Cost Range (USD) | Cost Range (EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Sensor Replacement | $150 – $300 | €130 – €260 |
| Exhaust Leak Repair | $100 – $400 | €85 – €345 |
| Catalytic Converter Replacement | $500 – $2,500 | €430 – €2,150 |
| Fuel Injector Cleaning/Replacement | $200 – $600 | €170 – €515 |
| Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement | $150 – $400 | €130 – €345 |
| Labor Costs (per hour) | $75 – $150 | €65 – €130 |
FAQS
How to Fix the P2097 Code
If you’ve diagnosed a faulty oxygen sensor as the cause of the P2097 code, the next step is replacing the sensor. This can be done with basic hand tools and an oxygen sensor socket.
After installing the new sensor, make sure to clear the trouble codes from the system to reset the vehicle’s diagnostics. This will help ensure that the issue is properly addressed and the vehicle runs efficiently again.
Is it Okay to Drive with the P2097 Code?
Driving with a P2097 code is not recommended, as it often points to a faulty oxygen sensor. Continuing to drive with this issue can cause stalls, lead to poor fuel economy, and even result in engine damage over time.
If left unchecked, it can also lead to pricey repairs down the road. It’s best to get the replacement sensors as soon as possible to avoid further damage and keep your vehicle running at its best.
What Causes a Fuel System to be Too Rich?
A fuel system can run too rich when it’s oversupplying the engine with too much fuel, causing a rich mixture. Common causes include a leaking fuel injector, which allows too much fuel to enter the engine, or high fuel pressure caused by issues like a pinched or clogged fuel return line. These conditions disrupt the balance of air and fuel, leading to an overly rich mixture.
Can a Bad O2 Sensor Cause a Rich Condition?
Yes, a bad O2 sensor can cause a rich condition. If the O2 sensor senses too much oxygen, it adjusts the fuel mixture to make it richer. This can lead to the engine running with an excess of fuel, creating problems with the catalytic converter and potentially causing other engine issues.
How to Repair O2 Sensors?
To repair or replace a faulty O2 sensor, start by performing an OBD 2 scan to confirm the issue. Once you’ve located the faulty sensor, the next step is to unscrew and unplug the old sensor. After removing it, replace it with a new sensor, making sure to avoid getting any grease on it, as this can affect the proper reading.

Mian Hashir is a passionate automotive enthusiast and the lead author at Car Garagee, a website dedicated to providing in-depth car reviews, maintenance tips, and the latest news in the automotive world. With years of experience in the industry, Hashir combines his technical knowledge with a love for cars to deliver insightful and engaging content. Whether you’re a car owner or a curious reader, Mian Hashir’s articles help readers make informed decisions, from choosing the right vehicle to understanding how to keep it in top condition.










