The P0430 trouble code is a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that signals a catalyst system efficiency below threshold in Bank 2. This means the catalytic converter, which is mounted near the engine, is not operating efficiently as it should. The vehicle’s on-board computer detects an issue through the O2 sensor, specifically the downstream oxygen sensor in bank two, which notices an irregularity in performance.
A faulty or damaged catalytic converter, O2 sensor, wiring issues, or exhaust leaks are common reasons for this code. When the problem arises, the check engine light becomes illuminated, the vehicle may stall, lose power, idle roughly, or belch smoke, and it may even fail an emissions test due to increased pollutants. The OBD-II diagnostics scanner can show an error, helping pinpoint if the issue is in the sensor, plug, or wiring. Since the converter is essential for reducing emissions, early diagnosis using the OBD-II connector and checking switches and logs before and after the issue is detected can prevent costly repairs and ensure the vehicle runs efficiently.
What Does the P0430 Code Mean?
The P0430 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) signals a problem with the catalyst system efficiency below threshold in Bank 2. This means the catalytic converter, mounted near the engine, on the opposite side of cylinder number one, is failing to break down pollutants effectively. As a result, oxygen (O2) levels in the exhaust decrease, and the downstream sensor detects the change. The vehicle computer then activates the check engine light (CEL) and logs the issue in the OBD-II diagnosis system.
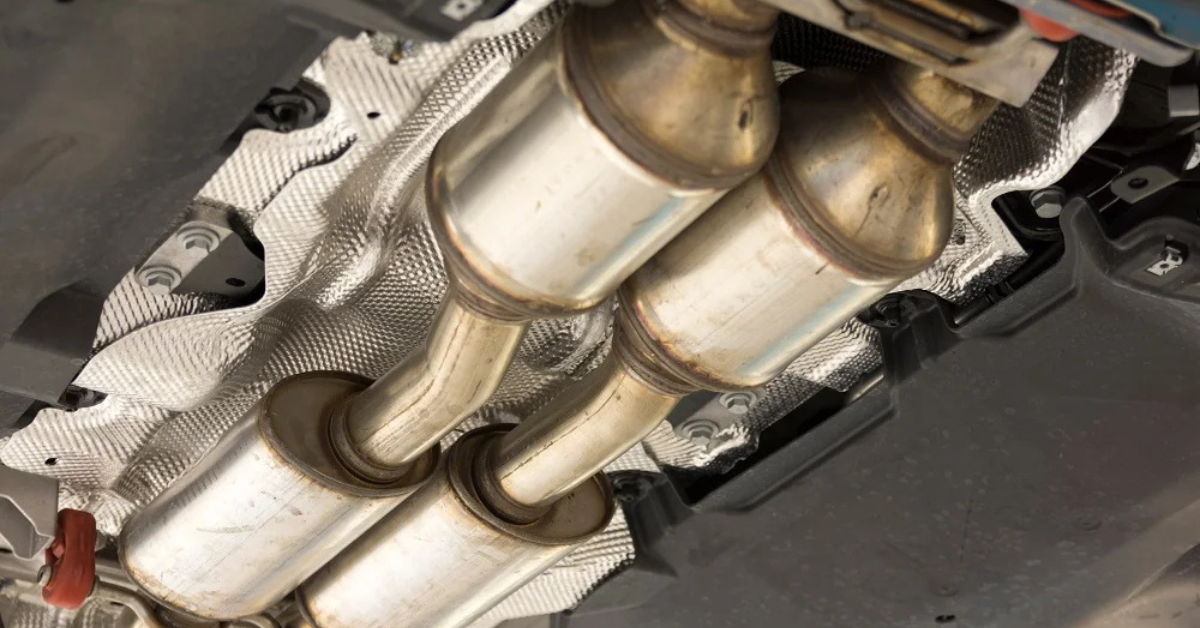

Ignoring this issue can lead to higher pollution, potential long-term damage, and may even violate state and federal emissions limits, especially in areas where vehicle emissions require testing. While the vehicle may continue to run fine, an internally obstructed or clogging catalytic converter can cause poor performance over time. A Pro Tip for car owners: If the CEL is illuminated, using a code reader can confirm if it’s P0430 or a related issue like P0420.
How the Catalytic Converter Works
The catalytic converter is an emissions control device mounted in the exhaust system that helps reduce harmful gases produced by the engine. It works by transforming pollutants into harmless substances like water vapor and carbon dioxide. This system targets three major enemy gases: NOx (nitrogen oxides), HC (hydrocarbons from unburned fuel), and CO (carbon monoxide)—a deadly poison that is both invisible and odorless in a closed space. The catalyst inside the converter helps break down these gases without undergoing change itself.
Modern three-way catalytic converters contain a hard clay honeycomb structure coated with fine particles of precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium, all surrounded by a vermiculite blanket for heat insulation. These catalysts heat up quickly, reaching around 1,000 degrees, with an optimal light-off temperature of 1,400 degrees. A healthy catalytic converter ensures too-rich mixtures are burned off properly, resulting in normal combustion products and a healthy CO2 balance.
If an issue arises, such as a P0430 or P0420 code, it indicates a problem where the converter’s light-off process is delayed, impacting its ability to clean emissions. The OBD-II system continuously monitors this performance through oxygen sensors, which are located both upstream and downstream of the converter. The PCM (computer) tracks these switching rates, and if both sensors show the same readings, it signals a failure.
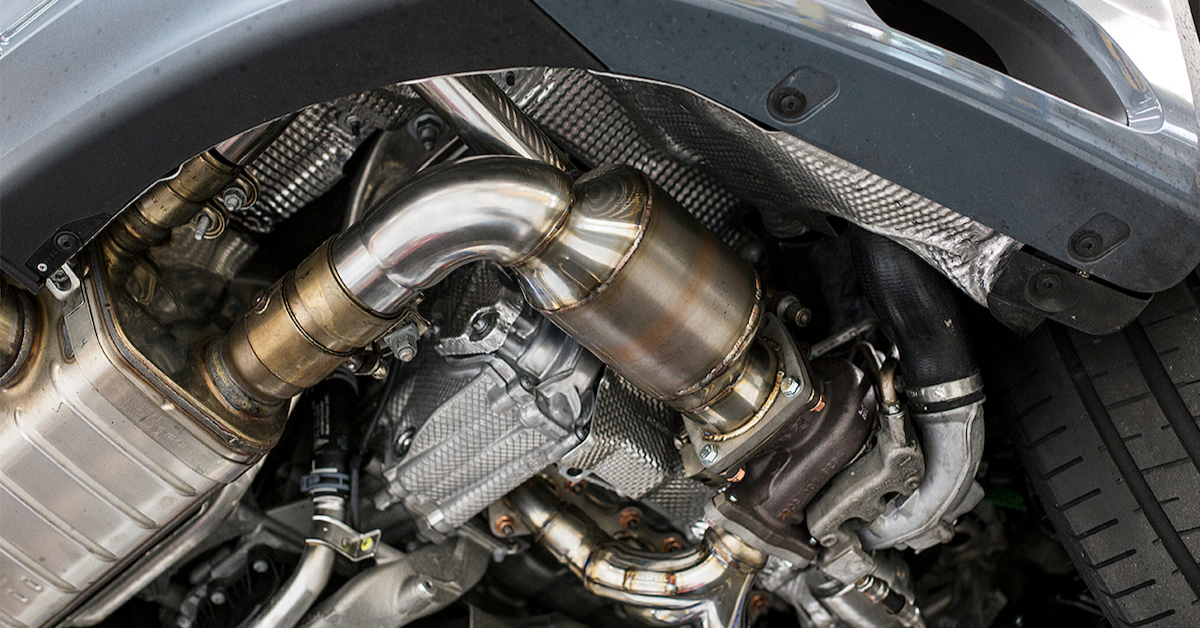
Advanced live data monitoring can be performed using a scan tool, smartphone app, or dongle connected to the DLC connector. A healthy converter efficiently produces CO2, and its heat helps warm the vehicle at startup, especially in cold weather. Since 1996, emissions regulations require PCM monitoring to ensure vehicles meet environmental standards, helping reduce pollution along grass roadsides, mowing plants, and trees with every gallon consumed.
P0430 vs P0420
The P0430 trouble code is a mirror image of P0420, but it applies to the catalytic converter in Bank 2, while P0420 is associated with Bank 1. These banks refer to different sides of the engine, and it’s worth noting that not all engines have two banks. In inline (straight-cylinder) configurations, there is usually one bank, whereas six-cylinder engines typically have two banks, each with its own catalytic converter (cats) and four O2 sensors.
For example, in a Jeep 4.0L, the engine tends to be configured in a way where the OBD-II scanner can distinguish between P0430 and P0420. However, since different causes can lead to a catalytic converter problem, it is always advisable to double-check the issue before making repairs. Vehicles such as BMWs may have unique code triggers, requiring precise diagnostics. Identifying the correct bank is critical to ensuring the right repair and preventing further engine issues.
What Are the Possible Causes of the P0430 Code?
The P0430 trouble code is often linked to a faulty catalytic converter, but there are other common issues that can trigger this OBD-II error. Below are some potential causes that mechanics investigate when diagnosing this code.
1. Damaged or Failing Catalytic Converter
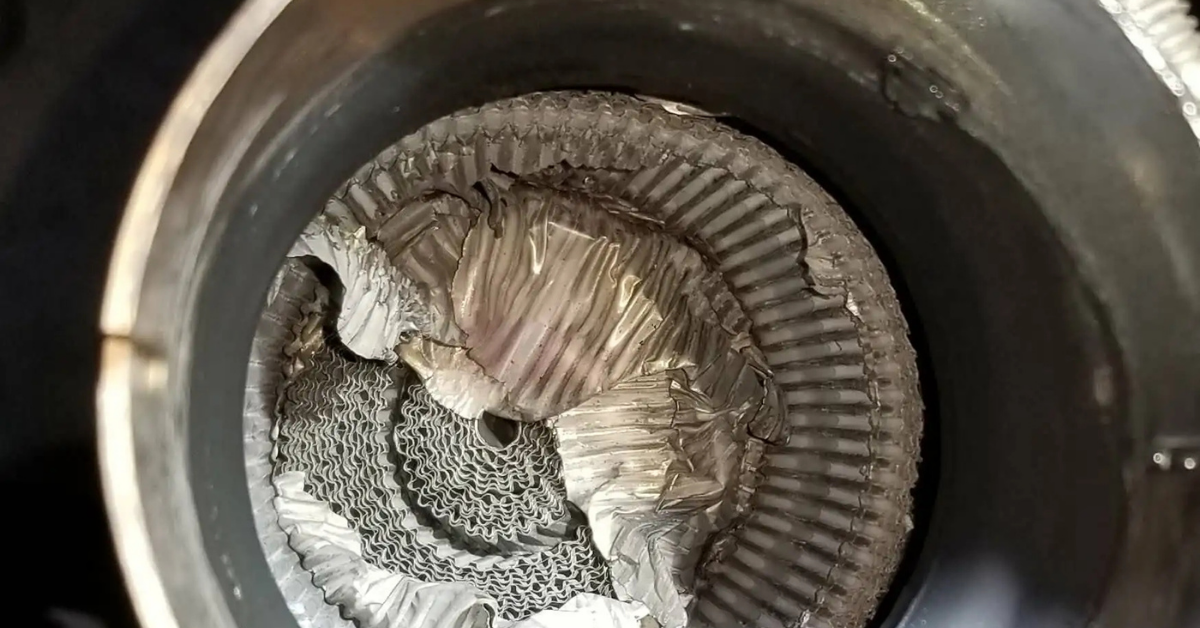

A frequent cause of P0430 is a failing catalytic converter, which may no longer be effectively processing emission levels. Over time, contaminants like coolant or oil can clog the converter, reducing efficiency. In extreme circumstances, an overheating converter can even glow cherry red, signaling raw fuel passing through due to an improper air-fuel ratio.
2. Faulty or Incorrect O2 Sensor Readings
A damaged O2 sensor can provide incorrect readings to the PCM (Powertrain Control Module), causing it to misinterpret the downstream and upstream sensors as reporting similar levels. This unreliable feedback signal can confuse the computer into logging a P0430 trouble code, even if the converter is still functioning.
3. Broken or Improperly Connected Wiring
If the wiring of the O2 sensor is broken or improperly connected, the sensor may not transmit accurate data, leading to P0430. The PCM detects abnormalities in the sensor’s output, assuming the converter is not working properly.
4. Exhaust System Leaks
A leak in the exhaust system, such as a crack in the manifold, loose header pipe, or other damaged components, can allow excess air to enter, which can confuse the fuel injectors and disrupt emissions readings. This may lead the PCM to incorrectly diagnose a catalytic converter failure.
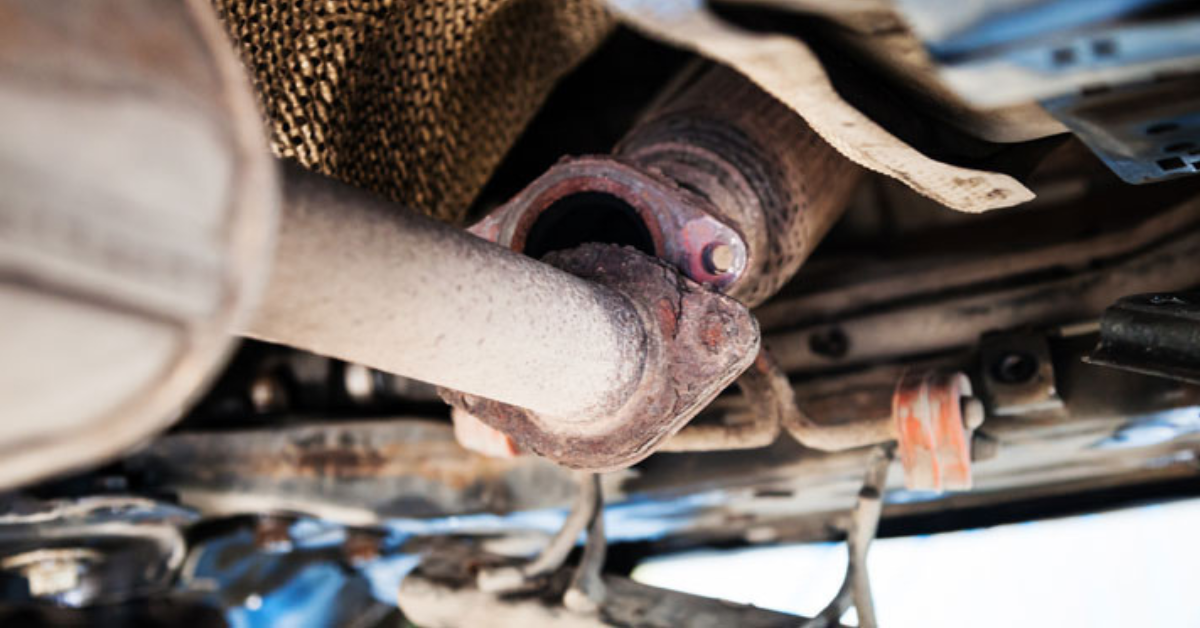

5. Engine Misfires and Improper Air-Fuel Ratio
An improper ratio of fuel to air can cause engine misfires, preventing the catalytic converter from heating up enough to work efficiently. This may lead to raw fuel passing through, damaging the converter and triggering P0430.
6. PCM Software Issues or Updates
In some cases, a computer software update may be required to correct how the PCM interprets fuel feedback signals. Some manufacturers release software patches to improve the converter’s performance monitoring, ensuring that the OBD-II system correctly identifies true failures rather than false readings.
Read More:
Walmart Tire Installation Cost [2024 Updated]
Valvoline Oil Change Prices List 2024 [Explained]
What Are the Common Symptoms of the P0430 Code?
If your vehicle has a P0430 trouble code, you may notice symptoms that affect drive quality and overall performance. Identifying these early can help prevent potential damage to the catalytic system.
1. Illuminated or Flashing Check Engine Light
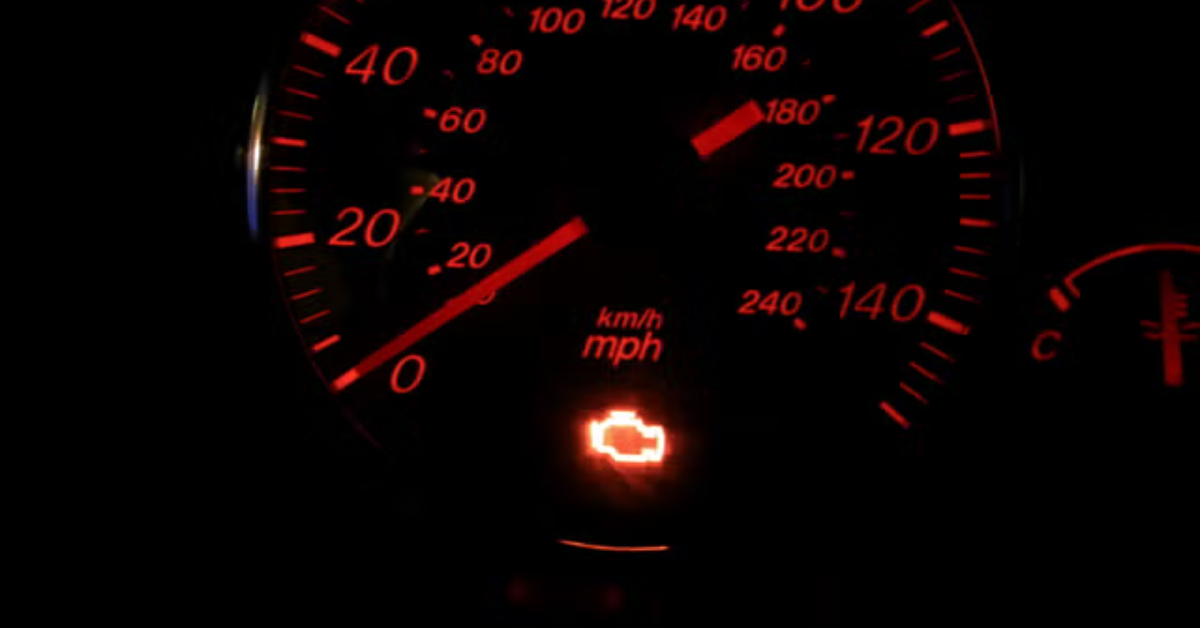

One of the first signs of P0430 is an illuminated or even flashing check engine light, signaling a problem with the catalytic converter’s function.
2. Failed Emissions Test
If the converter is worn, degraded, or obstructed, it won’t effectively reduce pollutants, leading to a failed emissions test.
3. Rotten Egg or Sulfur Smell
A rotten egg sulfur smell indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning properly, which can happen when it’s internally blocked, clogged, or damaged.
4. Lack of Power and Rough Idle
A clogged or degraded converter can lead to performance problems, causing a lack of power, rough idle, or even stalling.
5. Oxygen Sensor Issues
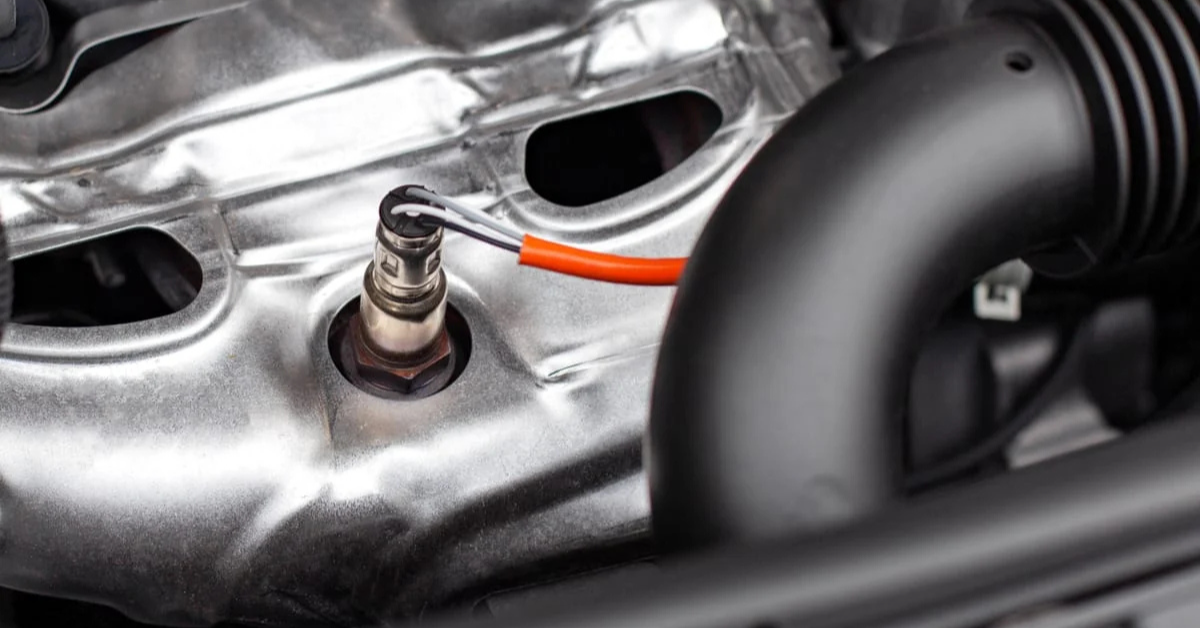

A damaged oxygen sensor can also contribute to P0430, as it may not accurately detect emissions levels, making the PCM misinterpret the converter’s efficiency.
6. Exhaust Leaks and Increased Noise
A possible cause of P0430 is an exhaust leak, which can increase noise and allow gases to bypass the muffler, affecting overall performance.
7. Cold Weather Start Issues
In cold weather, you may experience longer warm-up times due to a worn-out catalytic converter, leading to inefficiencies in the exhaust system.
How to Fix the P0430 Code
The P0430 code is stored due to multiple reasons, so there is no magic bullet fix. To diagnose accurately, start with an OBD-II scanner to see if it’s also showing P0420, as both DTCs could mean a bad catalytic converter. If the converter is clogged with emissions buildup or rendered useless due to extensive damage, it needs to be replaced.
A faulty oxygen sensor can also cause issues, so it’s important to inspect the wiring harness, connectors, and any loose electrical connection that may be damaged, frayed, or dirty. An exhaust system leak should be checked for a crack, rusted spot, or other damage, and depending on the severity, you may need to fix the source or replace a pipe length or the entire system.
Consult factory repair information, as vehicles have different applications, and contamination from oily grime can diminish effectiveness. After completing the necessary repairs, use a scan tool to reset the error and check if the problem is resolved with the proper solution.
FAQS
What Does Code P0430 Bank 2 Mean?
The P0430 error code occurs when the downstream oxygen sensor in Bank Two notices an irregularity in catalytic converter performance. This means the system is operating below the efficiency threshold, signaling that this essential component is not reducing emissions properly. If left unresolved, it can lead to higher pollutant levels and potential engine performance issues.
What Is the Most Common Cause for a P0430 Code in Ford?
A faulty catalytic converter is the most frequent cause of the P0430 trouble code in Ford vehicles. When the converter fails, it no longer effectively processes emissions, leading to increased pollutants and triggering the check engine light. A proper OBD-II scan and mechanical inspection can help determine if replacement is needed.
Can a MAF Sensor Cause a P0430?
The MAF sensor, located in the air intake duct, can contribute to P0430 and P0420 complaints by affecting the catalytic converter’s efficiency. A malfunctioning MAF sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to unburned fuel entering the converter, making it work inefficiently.
This issue is notorious in aging Toyota engines, where a failing MAF sensor can cause cat codes soon after the engine starts. Proper diagnosis is necessary to avoid unnecessary converter replacements.
How to Clean a Catalytic Converter?
The best way to clean a catalytic converter is by using a dedicated oil degreaser product or a strong cleaner. A mixture of dish soap and warm water in a large bucket can also work best if the converter fits inside. Fully submerge it and let it sit overnight to break down built-up residue. This method can help restore some efficiency but may not work if the converter is severely clogged or damaged.
Can You Drive with P0430?
While you can drive with the P0430 code, it is essential to visit a mechanic soon. Ignoring this issue can cause serious problems, including catalytic converter damage, failed emissions tests, and costly replacements. A failing converter can also reduce performance and negatively impact fuel economy, making early diagnosis and repair crucial.
How to Check O2 Sensors?
To test an O2 sensor, start your vehicle and locate the signal wire. Use a voltmeter set to the 1-volt scale and check if the voltage fluctuates between 200 and 800 millivolts (0.2 to 0.8 volts). If the meter shows a steady reading or does not fluctuate properly, the sensor may be faulty and require replacement to ensure the engine is running efficiently.
How to Remove a Catalytic Converter?
If the converter is bolted to the exhaust system, it can be carefully removed with the right tools. However, if it is welded, you may need to physically cut the pipes connected to it. Professional mechanics typically use a Sawzall tool or a specialized exhaust cutter to safely remove welded converters. Proper removal ensures that the new converter fits correctly and functions as intended.

Mian Hashir is a passionate automotive enthusiast and the lead author at Car Garagee, a website dedicated to providing in-depth car reviews, maintenance tips, and the latest news in the automotive world. With years of experience in the industry, Hashir combines his technical knowledge with a love for cars to deliver insightful and engaging content. Whether you’re a car owner or a curious reader, Mian Hashir’s articles help readers make informed decisions, from choosing the right vehicle to understanding how to keep it in top condition.