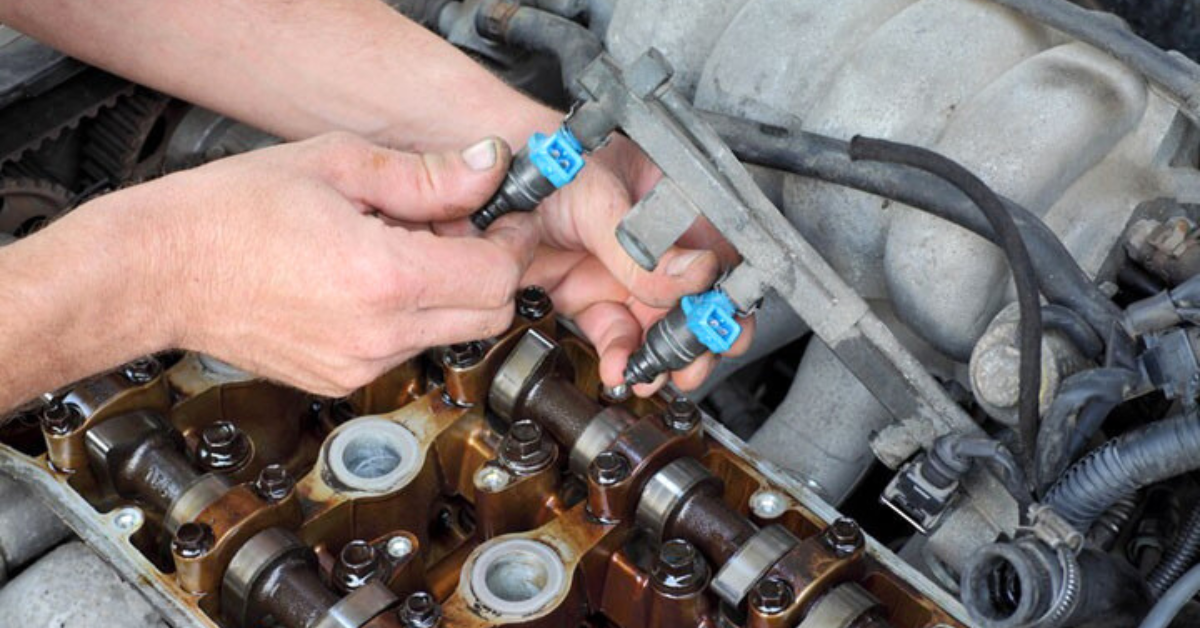
The P2096 error code signifies a critical issue with the vehicle’s post-catalyst fuel trim system, specifically indicating a lean condition on Bank 1. This system is responsible for regulating the fuel-to-air mixture after the exhaust gases have passed through the catalytic Converter. A lean condition means that the vehicle is receiving too much air and insufficient fuel, potentially leading to poor fuel efficiency and reduced engine performance.
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is part of a broader set of powertrain codes—including P2097, P2098, and P2099—that relate to the fuel trim system. When the engine control module (ECM) or powertrain control module (PCM) detects that the air-fuel mixture is outside the ideal range, typically due to improper fuel delivery or sensor malfunctions, it triggers the P2096 code. The issue often arises in Bank 1, which refers to the side of the engine that contains the number one cylinder. This could occur in vehicles with V-6 or V-8 engines.
More About the P2096 Code
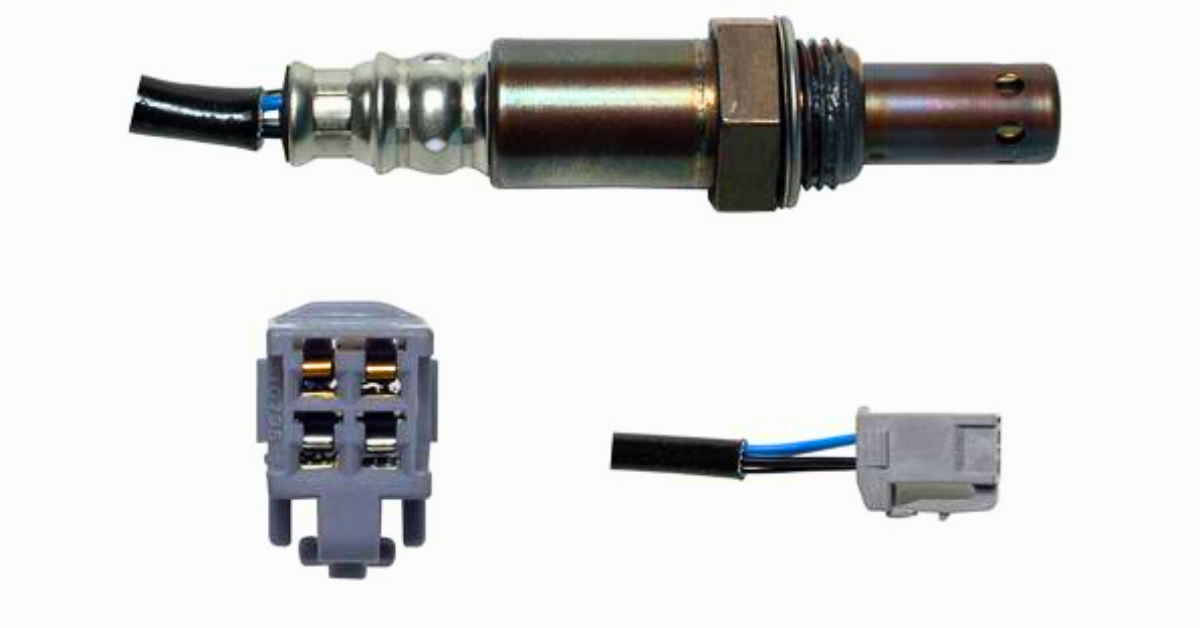
The P2096 code affects the vehicle’s air-fuel ratio, which is vital for engine performance. The downstream oxygen sensor, also known as the post-catalyst sensor, monitors the efficiency of the catalytic Converter by measuring the exhaust gases after they have passed through the Converter. This sensor ensures that the air-fuel mixture is regulated adequately for efficient combustion.
Additionally, the upstream oxygen sensor (or pre-catalyst sensor) measures the byproducts of the combustion process to ensure the engine receives the correct fuel-air charge. When the mixture is off, it can result in either a lean condition (too little fuel) or a rich condition (too much fuel). If the downstream sensor in Bank 1 detects such issues, it triggers the P2096 code, signaling an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture after the catalytic Converter.
Components Related to P2096
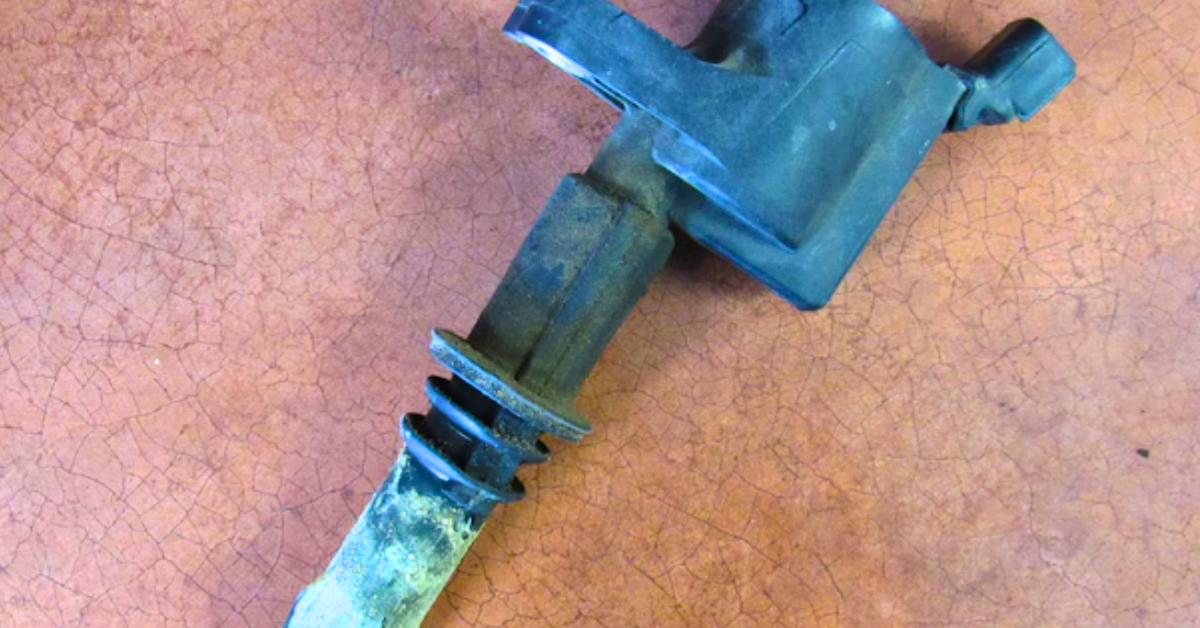
The downstream oxygen sensor, located after the catalytic Converter, plays a key role in monitoring the efficiency of the catalytic Converter. It provides feedback to the powertrain control module (PCM), helping to adjust the air-fuel ratio to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce harmful emissions.
Additionally, the fuel injectors and fuel pressure regulator are critical components that affect the vehicle’s fuel system and can influence the performance of the downstream O2 sensor. Exhaust system leaks can also lead to inaccurate oxygen levels, disrupting the sensor’s ability to regulate the proper air-fuel ratio and further impacting engine performance and emissions control.
Symptoms of P2096
The P2096 code can trigger several noticeable symptoms that can affect the vehicle’s overall performance. One of the most common indicators is the check engine light, which illuminates to alert the driver to an issue. Other symptoms include poor acceleration, a rough idle, and poor gas mileage, all of which are caused by the incorrect fuel-air mixture resulting from the lean condition detected by the oxygen sensor.

If the problem is left unaddressed, it can lead to more severe issues, such as engine misfires, a red-hot catalytic converter, and even internal engine damage. The engine control module (ECM) may attempt to enrich the fuel mixture by adding unnecessary fuel to compensate, which can result in degraded fuel economy. If the mixture remains out of balance, the Converter can overheat, leading to further contamination and damage.
Symptoms of P2096 – Key Points:
- Check engine light turns on.
- Poor acceleration and rough idle.
- Poor gas mileage and fuel economy drop.
- The engine misfires and produces a lean mixture in the fuel system.
- The red-hot catalytic Converter indicates indicates overheating.
- Unmetered air enters the system, resulting in a fuel imbalance.
- The fuel-air mixture is becoming inefficient, potentially causing engine damage.
The computer needs to adjust the mix, which adds unnecessary fuel.
These symptoms point to a need for timely diagnosis and repair to prevent long-term damage.
Possible Causes of P2096

The P2096 code typically arises from issues with the vehicle’s fuel system, oxygen sensors, and exhaust system. Below is a detailed explanation of the most common causes:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can provide inaccurate readings, which affects the fuel-to-air mixture and triggers the P2096 code.
- Catalytic Converter Issues: A clogged, melted, or disintegrated catalytic Converter can impair the downstream oxygen sensor’s ability to measure exhaust gases, resulting in a lean mixture and a P2096 code.
- Exhaust Leaks: Exhaust leaks, particularly upstream of the downstream O2 sensor, can cause incorrect oxygen readings and trigger the P2096 code.
- Fuel Pressure Problems: Low fuel pressure, caused by a failing fuel pump or a faulty fuel pressure regulator, can create an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture, resulting in the P2096 error.
- Air or Vacuum Leaks: Unmetered air from air leaks or vacuum leaks can affect the engine’s fuel-to-air ratio, triggering the P2096 code.
- Clogged Fuel Filter: A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow, resulting in inadequate fuel delivery and an imbalanced fuel-air mixture, which may cause the P2096 error.
- Mass Airflow Sensor Issues: A malfunctioning Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor or an MAF circuit malfunction can lead to incorrect air flow readings, resulting in improper fuel mixture adjustments.
- Leaking Fuel Injectors: Leaking fuel injectors can cause too much fuel to be injected into the engine, disrupting the fuel-air mixture and triggering the P2096 code.
Images are for illustrative purpose only; credits belongs to
Car Services in Reading
Each of these causes, if left unchecked, can lead to significant issues with your vehicle’s engine performance and emissions, potentially resulting in costly repairs if not addressed promptly. Diagnosing the exact cause typically requires professional expertise, as these problems can stem from several interconnected components.
Potential Solutions for P2096
1) Use an OBD-II Scanner: Begin by using an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the P2096 code and any additional codes that may provide more insight into the issue. This will help identify the underlying problem more accurately.
2) Check the Exhaust System: Inspect the exhaust system for cracks, missing gaskets, rust holes, or loose parts. These issues can affect the oxygen sensor readings, leading to the P2096 code.
3) Inspect Electrical Connectors: For vehicles like Jeep or Chrysler models, check the electrical connectors around the oxygen sensor. Loose or corroded connections can prevent proper sensor function, triggering the error code.
4) Test the Oxygen Sensor: If the oxygen sensor has a heater circuit malfunction or is faulty, replace it. If a P2098 code indicates fuel contamination, consider using a higher-grade fuel to ensure cleaner combustion and improve sensor performance.
5) Check the Mass Airflow Sensor: A malfunctioning Mass Airflow sensor can lead to improper airflow readings, resulting in an incorrect air-fuel mixture. If the sensor is damaged, it may need to be replaced.
6) Inspect Cylinders and Plugs: Perform a cylinder test by spraying water on the cylinder exhaust port. If the water evaporates slowly, it indicates a misfire. Check the plugs and plug wires to ensure they’re functioning correctly.
7) Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Utilize advanced diagnostic tools, such as the Tech II or Snap-On Vantage, to gather real-time information and accurately diagnose whether the oxygen sensor is malfunctioning.
8) Check for Leaks in the Intake Manifold: Leaks in the intake manifold can introduce unmetered air, affecting the air-fuel ratio. Look for a whistling sound that may indicate these leaks and repair them.
9) Reprogram ECM or Replace Oxygen Sensor: If later-model Jeeps experience programming issues, updating the Engine Control Module (ECM) may be necessary. If the oxygen sensor is damaged, replace it as per the vehicle’s 8-year, 80,000-mile warranty.
These steps provide a comprehensive approach to fixing the P2096 error code and ensuring your vehicle runs efficiently.

HotRod.
Risk Assessment:
| Risk Factor | Low Risk | Moderate Risk | High Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Damage Potential | Intermittent code with no drivability issues | Consistent code with minor symptoms | Persistent code with noticeable performance issues |
| Emissions Impact | Temporary code occurrence | Occasional code appearance | Continuous fault presence |
| Repair Urgency | Can schedule repair in coming weeks | Should address within days | Immediate attention required |
| Cost Escalation Risk | Low chance of causing additional damage | May lead to secondary issues if ignored for weeks | Can quickly cause expensive component failures |
How Easy Is It to Diagnose a P2096 Code?
Diagnosing the P2096 code can be challenging, as it often involves fuel delivery issues that don’t immediately point to a specific problem. The issue may stem from various components such as the downstream O2 sensor, fuel injectors, or exhaust system. Proper diagnostics require a series of tests and an understanding of the vehicle’s functions, which is why experts with access to the right tools are best suited to handle them.
Diagnostic Procedure:
- Scan for Codes: Use a scan tool to retrieve P2096 and related codes and document any freeze frame data.
- Examine the Exhaust System: Inspect for exhaust leaks or issues with the downstream O2 sensor. Check if the sensor’s voltage cycles between 0.1 V and 0.9 V. If it stays above 0.45 V, suspect an exhaust leak or a failed catalytic converter.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Measure the fuel pressure to ensure it falls within the specified range of 30-60 psi (200-410 kPa). Low or high pressure may indicate a problem.
- Injector Leak Test: Perform an injector leak test to identify leaking injectors and address any fuel delivery issues.
- Smoke Test: Conduct a smoke test on the intake system to identify any vacuum leaks that could affect the air-fuel mixture.
- Replace Components as Needed: If all other components check out, replace the downstream oxygen sensor if it’s faulty or not functioning correctly.
Estimated Repair Costs
Depending on the underlying cause, repair costs for P2096 can vary significantly:
Repair Cost (USD) Cost (EUR)
| Repair | Cost (USD) | Cost (EUR) |
| Diagnostic Fee | $75-$150 | €100-€200 |
| O2 Sensor | $50-$200 each | €70-€250 each |
| Catalytic Converter | $300-$2000 | €400-€2500 |
| Exhaust Repairs | $50-$300 | €70-€400 |
| Fuel Injectors | $50-$1200 | €70-€1500 |
| Fuel Pump | $200-$1000 | €250-€1250 |
How Serious Is the P2096 Code?

Parts Avatar.
The P2096 code is a serious issue as it directly affects the air-fuel mixture, which is crucial for the vehicle’s performance. An imbalanced mixture, whether leaner or richer, can lead to significant engine concerns, including decreased fuel efficiency and potential damage to key components, such as the catalytic Converter.
If left unaddressed, the problem can escalate, leading to more severe issues that could affect the engine’s overall function. It’s essential to consult an expert for proper testing and prompt problem resolution to prevent long-term damage and costly repairs.
Can I Still Drive with a P2096 Code?
You can physically drive your vehicle with the P2096 code for a short term, especially if it’s the primary code and there are no major drivability issues. However, if the check engine light is flashing or if you experience symptoms such as rough running, power loss, or hesitation, it’s best to avoid driving and stop immediately to prevent engine damage and damage to the Catalytic Converter.
The root cause of the issue should be diagnosed and fixed promptly to avoid further complications. If the vehicle’s performance worsens, consider having it towed to a mechanic to prevent additional damage.
Frequently Asked Questions About P2096
- How do I fix code P2096? Fixing P2096 involves checking and replacing a faulty oxygen sensor, inspecting for exhaust leaks, and ensuring proper fuel pressure and fuel injectors.
- Can I still drive with a P2096 code? Driving with P2096 is possible for a short period, but it can cause engine damage and poor fuel efficiency; therefore, it’s best to address the issue promptly.
- How do I fix a system that is too lean? To fix a lean system, check for vacuum leaks fuel injector issues, and ensure the oxygen sensors and fuel pressure are functioning correctly.
- What causes the post-catalyst fuel trim system to lean in Bank 1? A faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks, fuel delivery problems, or a malfunctioning catalytic converter often cause post-catalyst fuel trim system issues in Bank 1.

Mian Hashir is a passionate automotive enthusiast and the lead author at Car Garagee, a website dedicated to providing in-depth car reviews, maintenance tips, and the latest news in the automotive world. With years of experience in the industry, Hashir combines his technical knowledge with a love for cars to deliver insightful and engaging content. Whether you’re a car owner or a curious reader, Mian Hashir’s articles help readers make informed decisions, from choosing the right vehicle to understanding how to keep it in top condition.