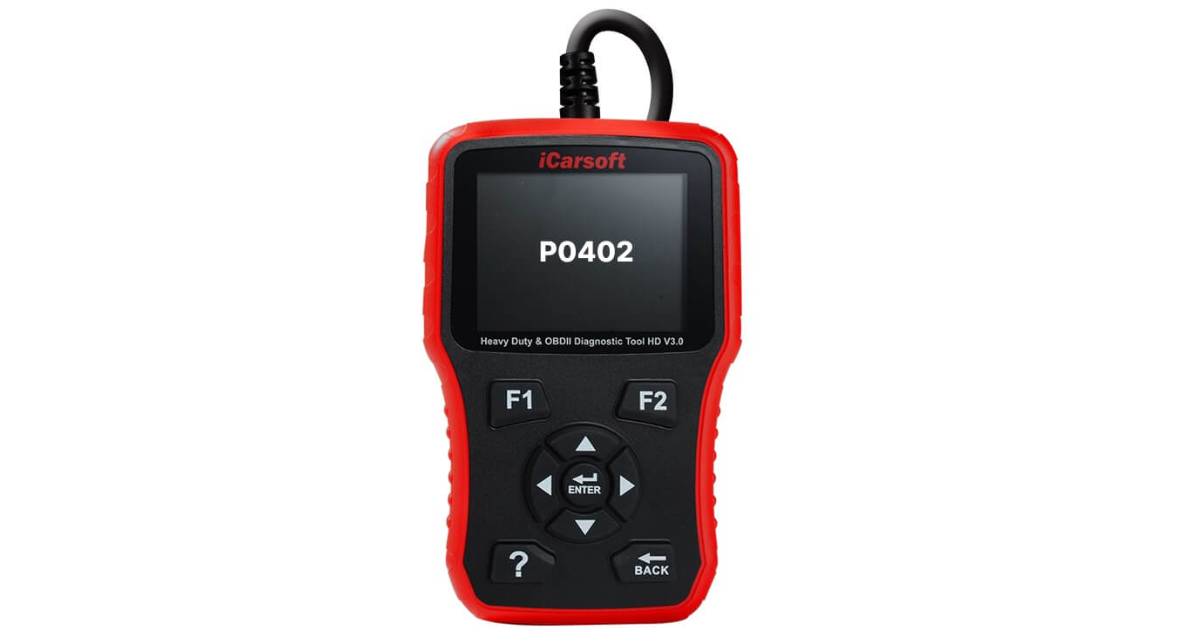
When my vehicle’s computer stored code P0402, I found out it means “Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Excessive Detected”—a common diagnostic trouble code tied to the EGR system. The exhaust gas recirculation process is supposed to help reduce emissions, but when it goes too far, it triggers this code.
The expert techs reviewed every part of the EGR system to locate the specific problem that caused the code to be stored in the car’s computer. After going through their repair orders, they explained how excessive EGR flow disrupts normal engine function. This isn’t just a light on your dash—it’s a sign your vehicle needs prompt attention.
Key Takeaways:
1) Code P0402 means there’s excessive exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow in the system, which affects engine performance and emissions.
2) Common causes include a malfunctioning EGR valve, blockage in the EGR passages, or too much back pressure in the exhaust.
3) Symptoms often show up as a rough running engine, Check Engine Light illumination, and emission test failure.
4) Proper diagnosis involves scanning for codes, doing visual inspections, and testing key components like sensors and valves.
5) Effective repairs may include replacing the EGR valve, cleaning carbon deposits, or repairing the exhaust catalyst—with professional assistance or alternative solutions recommended in tougher cases.

Fixmycar.pk
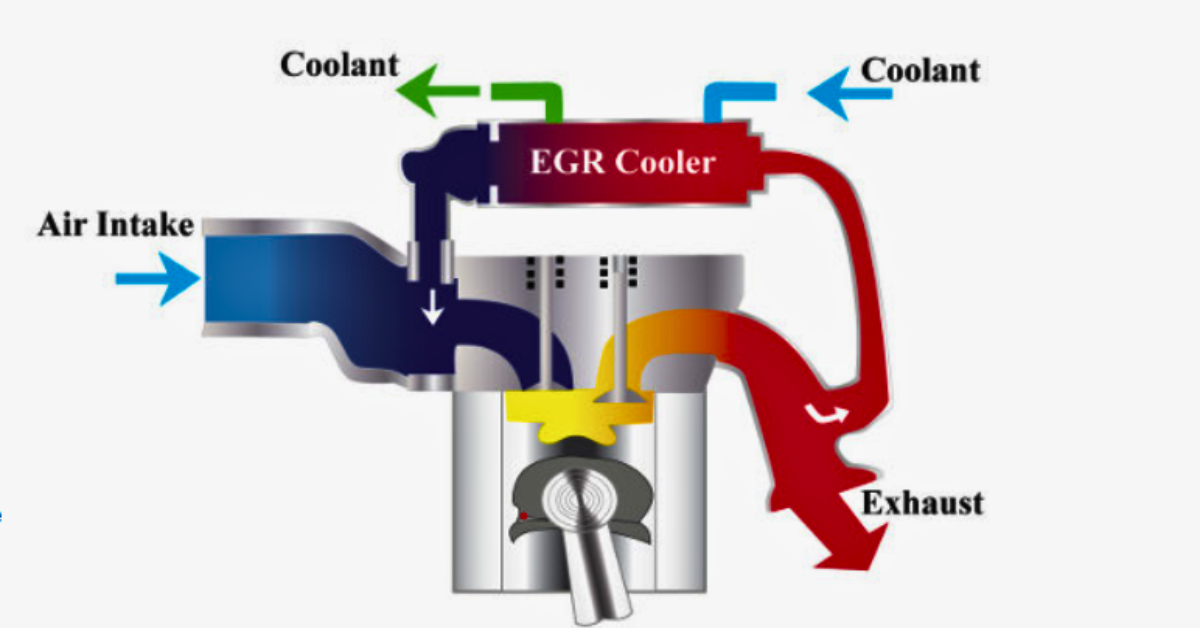
What the EGR System Consists Of?
The EGR system in my car was made up of three main parts: the EGR valve, an actuator solenoid, and a differential pressure sensor (DPFE). Together, they regulate how much exhaust gas is recirculated or re-burned inside the engine.
A failure in any of these components can cause code P0402 to trip, especially when the exhaust system is affected. Learning this from a detailed article helped me understand why even one faulty part can throw off the balance.
What Does Code P0402 Mean?
When my vehicle went in for a diagnostic scan, it showed code P0402, which means the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system is sending too much exhaust gas back into the engine. This system helps the engine run efficiently, consume less fuel, and emit fewer emissions by recycling exhaust gas into the intake system.
The exhaust gas mixes with intake air inside the combustion chambers, reducing oxygen levels, which lowers combustion temperatures and limits hazardous nitrogen oxide gas as a byproduct. The system is controlled electronically or by vacuum, depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and age, and when the ECM (Engine Control Module) detects a problem, it stores the code and turns on the check engine light.
Why Does the Code Trip?
In my Toyota, the P0402 code tripped because the EGR valve was stuck open, possibly due to carbon blocking or the valve being damaged. Sometimes, excessive vacuum or a faulty DPFE sensor causes the system to push too much exhaust back into the engine.
Before trying to replace parts, I checked the voltage while the car was running, compared it to the values in Toyota’s repair manual, and confirmed the need for replacement. I also had to remove the bypass tube, inspect for obstructions or vacuum leaks, and clean or replace necessary components to fix the issue.
What Causes Code P0402?
Understanding the causes of code P0402 is essential for proper diagnosis and repair. This code is usually triggered when the EGR system allows too much exhaust gas into the intake manifold. Below are the main causes, explained clearly:
Key Causes of P0402:
1) Defective EGR Valve
The EGR valve may be stuck open, damaged, or worn out, allowing constant exhaust flow, which results in excessive EGR operation.
2) Excessive Vacuum or Electrical Input
Too much vacuum or a malfunctioning electrical signal can force the EGR valve to stay open longer than needed.
3) Faulty Differential Pressure Feedback (DPFE) Sensor
This sensor measures the pressure in the EGR system. If it’s faulty, it may falsely report high flow, triggering the P0402 code.
4) Bad EGR Vacuum Solenoid
A bad solenoid can fail to control the vacuum pressure properly, leading to uncontrolled EGR flow.
5) Plugged Catalytic Converter with Excessive Back Pressure
A clogged converter increases back pressure, which forces more exhaust through the EGR valve than necessary.
6) Defects in EGR Volume Control Valve
If the volume control valve is stuck open, it can let too much gas pass into the intake.
7) Shorted or Open Solenoid Valve Harness
Electrical issues, like a short or open circuit, can stop proper communication between the ECU and EGR components.
8) Flaws in EGR Temperature Sensor or Circuit
A faulty temperature sensor or wiring circuit may cause the system to think there’s not enough temperature change, leading the ECU to overcompensate.
Symptoms Associated with Code P0402

Fixmycar.pk
Here are the key symptoms you may notice when your vehicle has code P0402:
- Check Engine Light Illumination
The check engine light may appear steadily or start flashing, serving as the first clear warning indicator. - Rough Engine Idle & Hesitation
The engine runs roughly, especially at idle. You may feel hesitation or misfires while driving. - Reduced Fuel Economy
Excessive EGR flow affects combustion, causing the engine to burn more fuel than necessary. - Stalling or Power Loss
You may experience engine stalling, lack of power, or slow acceleration under load. - Exhaust Leaks or Increased Vibrations
There might be visible exhaust leaks in the EGR system or increased engine vibrations due to improper exhaust flow. - Emission Test Failure
Because the engine isn’t burning fuel cleanly, the vehicle can fail emissions testing easily. - Exacerbated Damage If Ignored
Leaving the issue unresolved can lead to severe complications, costly repairs, and long-term engine damage.
Diagnosing the P0402 Code
- Start with a Diagnostic Scan
Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve code P0402 from the vehicle’s ECM. Also, document freeze frame data to understand the conditions when the code was triggered. - Clear Codes and Perform a Road Test
After clearing the code, take the car for a road test and monitor if the code reappears. If it does, the issue is still present and needs further inspection. - Conduct a Visual Inspection
Check all vacuum hoses, wiring, and connections to the EGR valve, control solenoid, temperature sensor, and back pressure transducer for leaks, damage, or loose fittings. - Check EGR Function and Catalyst
Verify if the EGR valve is functioning correctly by testing vacuum control or solenoid operation. Also, inspect the exhaust catalyst for signs of blockage or pressure buildup. - Look for Internal Obstructions
If needed, remove the EGR valve and components for a closer inspection. Look for carbon buildup, blockage, or anything hindering proper flow that could be the root cause.
Common Mistakes When Diagnosing the P0402 Code
- Replacing the EGR Valve Prematurely
One of the biggest mistakes is replacing the EGR valve without checking the pressure transducer, which plays a crucial role in regulating the system. - Overlooking Carbon Buildup
Failing to see if the EGR valve is held open by carbon deposits can lead to unnecessary repairs. Always inspect and clean before replacing parts. - Ignoring Minor Signs
Skipping small signs like loose wiring, vacuum leaks, or sensor faults can cause inaccurate diagnoses and miss the root cause of excessive EGR flow. - Not Following Proper Steps
Skipping steps like reviewing freeze frame data, or failing to perform a road test, can make it harder to accurately pinpoint the issue. - Lack of Confidence in Troubleshooting
Sometimes, not taking the time to understand the system fully results in misjudged repairs. Diagnosing with confidence and attention to detail saves time, money, and vehicle performance in the long run.
This Guide Will Help You Diagnose the P0402 Code Accurately
To diagnose code P0402 accurately, start with an OBD-II scanner to retrieve and scan the codes, then document freeze frame data. This gives you clear information about the conditions when the code was triggered. After that, clear the codes and take the vehicle for a road test to see if the issue returns, indicating a persistent or intermittent problem.
Next, perform a full visual inspection of vacuum hoses, wiring, and connections going to the EGR valve, control solenoid, temperature sensor, and back pressure transducer. Check for disconnection, damage, or excessive flow issues. If needed, test for back pressure in the exhaust catalyst, and inspect for carbon buildup or blockage—clean or replace any faulty components to ensure proper EGR function and restore optimal engine performance.
Tip: Quick Way to Check the EGR Valve
Olathe Toyota Logo
Use a hand vacuum pump to manually apply vacuum to the EGR valve and observe its response. If the valve opens and closes smoothly, it means the mechanical operation is normal. This quick test can help rule out valve issues before diving deeper into diagnostics.
Severity of the P0402 Code
The severity of code P0402 can vary depending on how the symptoms appear. In mild cases, it may just cause a rough engine idle, slight hesitation, or Check Engine Light without major drivability issues. But when the EGR valve allows excessive flow, it can lead to stalling during acceleration and reduced performance.
If the catalyst becomes blocked, it could result in engine power loss or the vehicle not starting at all. That’s why prompt diagnosis and repair are essential—not only to prevent further damage, but also to restore proper operation and ensure your car passes emission testing.
Replace or Repair These Parts to Fix OBD Code P0402
When I faced code P0402, I learned that resolving excessive EGR flow often requires a mix of repairs and part replacements. In many cases, a faulty EGR valve, cracked gasket, or carbon buildup in the bleed port was the root cause. By cleaning the carbon deposits and replacing damaged parts like the EGR valve or gasket, I was able to restore the normal flow of exhaust recirculation and get my car running right again.
Sometimes the issue goes deeper. A broken catalytic converter, faulty MAP sensor, or a failing engine coolant temperature sensor can all contribute to improper engine behavior and trigger code P0402. These components should be inspected for defects, especially if the code keeps appearing even after minor repairs. Replacing the oil pressure sender, Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor, or even a crankshaft position sensor may be necessary to correct the system’s response and optimize engine performance.
If you’re unsure where to start, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic and refer to the vehicle’s repair manual for accurate steps. A trained eye can identify if the excessive EGR flow is due to a stuck EGR valve, a vacuum leak, or something more complex like electrical issues in the control system. Tackling the underlying cause with targeted repairs ensures your vehicle operates optimally and avoids future issues.
How to Correct P0402: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Excessive Detected
To correct code P0402, you need to address the excessive exhaust gas recirculation flow by checking all related components. Start by inspecting the EGR valve—if it’s stuck open, it should be replaced or cleaned thoroughly to remove carbon buildup. Sometimes, simply cleaning the valve and restoring movement resolves the issue without deeper repairs.
If that doesn’t solve it, move on to the EGR temperature sensor and test for abnormal temperature changes, which may indicate faulty readings. A broken exhaust catalyst can also create backpressure, forcing excess gas into the intake. In this case, replacing the catalyst is necessary. Don’t forget to inspect the backpressure control valve as well—if it’s not working per the requirement, it could be a hidden cause.
Other related parts like the Throttle Position Sensor, Mass Air Flow Sensor, or using a proper sensor cleaner can also help restore system balance. Each of these plays a role in managing air-fuel mix and exhaust regulation. Fixing the fault code means taking a system-wide view and targeting each possible failure point to ensure the engine performs efficiently again.
How Serious Is Code P0402?
The seriousness of code P0402 depends on how long the issue is left unresolved. While it may not immediately cause major drivability problems, it often leads to a rough engine idle, hesitation, or even stalling when trying to accelerate. These symptoms can make the vehicle unpredictable and uncomfortable to drive.
More importantly, if the check engine light stays on, your vehicle may fail an emissions test, which can prevent registration renewal in many areas. A clogged catalytic converter caused by unaddressed EGR issues may result in power loss or even a complete engine failure to start, making timely repair not just smart—but necessary.
Professional Assistance for the P0402 Code
If the P0402 code persists after all normal repair attempts have been exhausted, it may be time to seek professional assistance. A qualified technician can offer a more accurate diagnosis using advanced tools and technical expertise to target the exact cause of excessive EGR flow. Their specialized knowledge often leads to more effective and lasting results than trial-and-error fixes.
In rare cases, an alternative solution involves uploading your Engine Control Unit (ECU) file to a portal that specializes in ECU tuning. This complex automotive process modifies the ECU’s software parameters to eliminate the error code permanently. While this should only be considered when other methods fail, it remains a viable option for restoring vehicle performance in hard-to-fix cases.
Estimated Repair Costs for P0402 Cause:
| Cause | Estimated Cost Range |
| Defective EGR Valve | $200 – $500 |
| Faulty DPFE Sensor | $100 – $250 |
| Bad EGR Vacuum Solenoid | $70 – $200 |
| Replacing Plugged Catalytic Converter | $500 – $2,000 |
| EGR Volume Control Valve Replacement | $150 – $400 |
| Solenoid Wiring Repair | $50 – $150 |
| EGR Temperature Sensor Replacement | $80 – $200 |
Note: Actual costs vary based on your vehicle model, labor rates, and parts availability.
Conclusion
Dealing with code P0402 means your engine is experiencing excessive flow of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), often due to a stuck open valve, a blocked vacuum diaphragm, or too much back pressure in the system. If left untreated, it can lead to long-term engine damage and poor vehicle performance. That’s why prompt diagnosis and repair are essential to keeping your car running smoothly.
The best approach is to consult a professional mechanic who can accurately identify the specific cause of the issue. They’ll inspect hoses, wiring, connections, and components like the control solenoid, temperature sensor, and pressure transducer to find the root of the problem. Once diagnosed, an expert repair will help resolve the issue effectively and restore optimal engine function.
If traditional repairs don’t fix the fault, alternative options like ECU tuning may be considered. This involves uploading the Engine Control Unit (ECU) file to a specialized portal to permanently remove the code. Taking the appropriate action not only solves the problem but also ensures smooth operation, helping your vehicle run efficiently and prolong its lifespan.
FAQ
1) How do you fix a P0402 code?
Fix P0402 by cleaning or replacing the EGR valve, checking vacuum lines, testing sensors, and inspecting the catalytic converter for blockage.
2) What causes excessive flow to the EGR valve?
Excessive flow is caused by a stuck-open EGR valve, faulty pressure transducer, carbon buildup, or excessive exhaust back pressure.
3) What are the symptoms of the code P0402?
Common symptoms include a check engine light, rough idle, stalling, poor fuel economy, and failed emissions test.
4) How to fix exhaust gas recirculation flow insufficient detected?
Clean or replace the EGR valve, check for clogged passages, test vacuum lines, and inspect the EGR control solenoid.

Mian Hashir is a passionate automotive enthusiast and the lead author at Car Garagee, a website dedicated to providing in-depth car reviews, maintenance tips, and the latest news in the automotive world. With years of experience in the industry, Hashir combines his technical knowledge with a love for cars to deliver insightful and engaging content. Whether you’re a car owner or a curious reader, Mian Hashir’s articles help readers make informed decisions, from choosing the right vehicle to understanding how to keep it in top condition.







