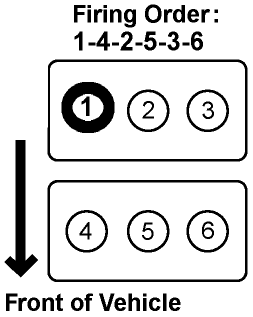
The Honda Odyssey, a popular minivan in the North American market, is known for its practicality, reliable engines, and strong performance. Since 1994, its V6 engine has delivered optimal power and efficiency, making it a desirable option for many drivers. However, understanding the firing order is crucial for upkeep, as it ensures smooth cylinder configurations, prevents misfire problems, and maintains long-term engine health.
Firing Order of the Honda Odyssey V6 Engine:
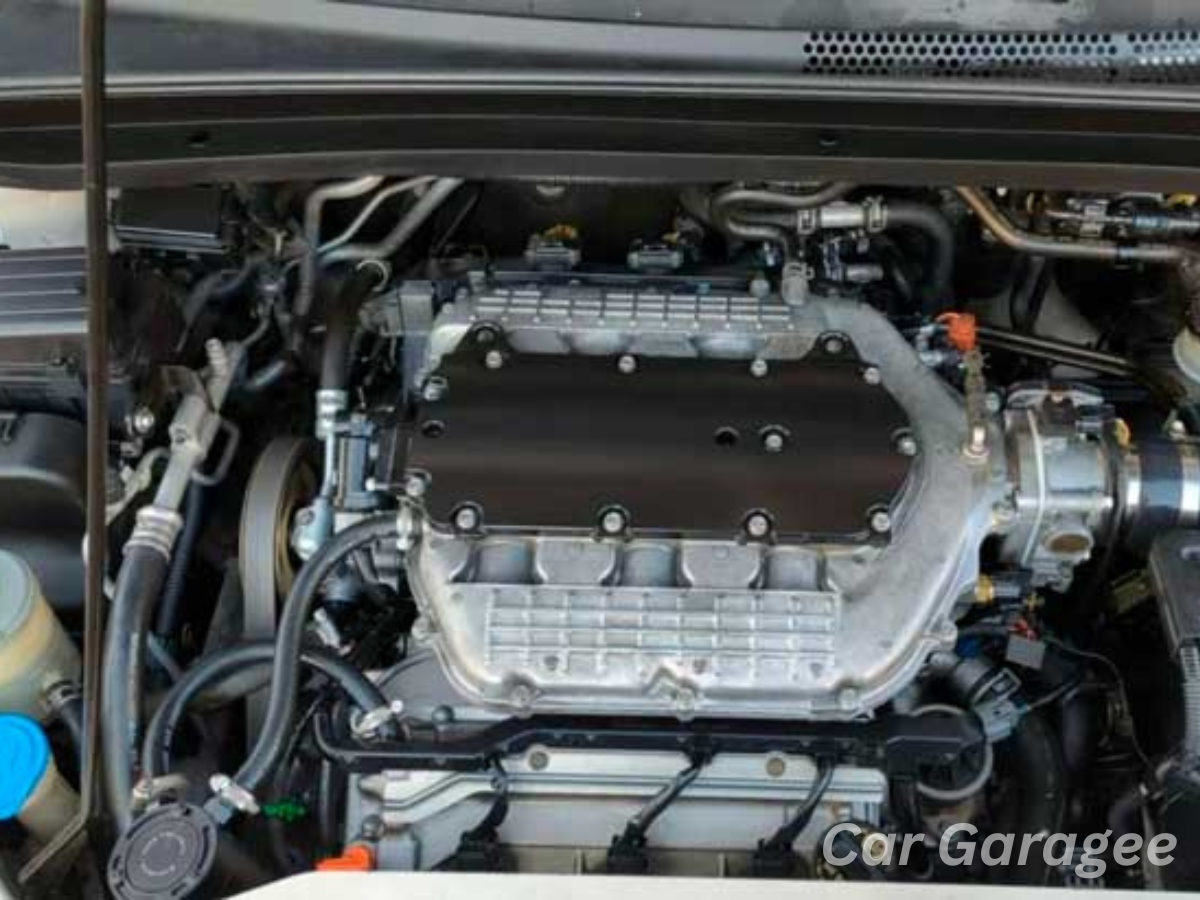
The firing order of the Honda Odyssey V6 engine (such as the 3.5L J35 V6) is 1-4-2-5-3-6. This sequence ensures smooth engine operation and balanced power delivery. The ignition starts at cylinder 1 (front passenger side), followed by cylinder 4 (rear driver’s side), cylinder 2 (front driver’s side), cylinder 5 (rear passenger side), cylinder 3 (middle passenger side), and finally cylinder 6 (middle driver’s side).
Cylinder Numbers in the Honda Odyssey
The Honda Odyssey’s cylinder numbering depends on the engine type. In a V6 engine (like the 3.5L J35 V6), the cylinder numbers are arranged in a banked layout. Bank 1 (passenger side) includes cylinders 1, 3, and 5, while Bank 2 (driver’s side) has cylinders 2, 4, and 6.
Cylinder 1 is at the front of the engine on the passenger side, which is crucial for diagnosing misfires or replacing spark plugs. Properly identifying cylinder numbers helps in troubleshooting engine issues and ensures accurate maintenance. Always refer to the Honda service manual for exact specifications related to your Odyssey’s model year.
Honda 3.5 firing order
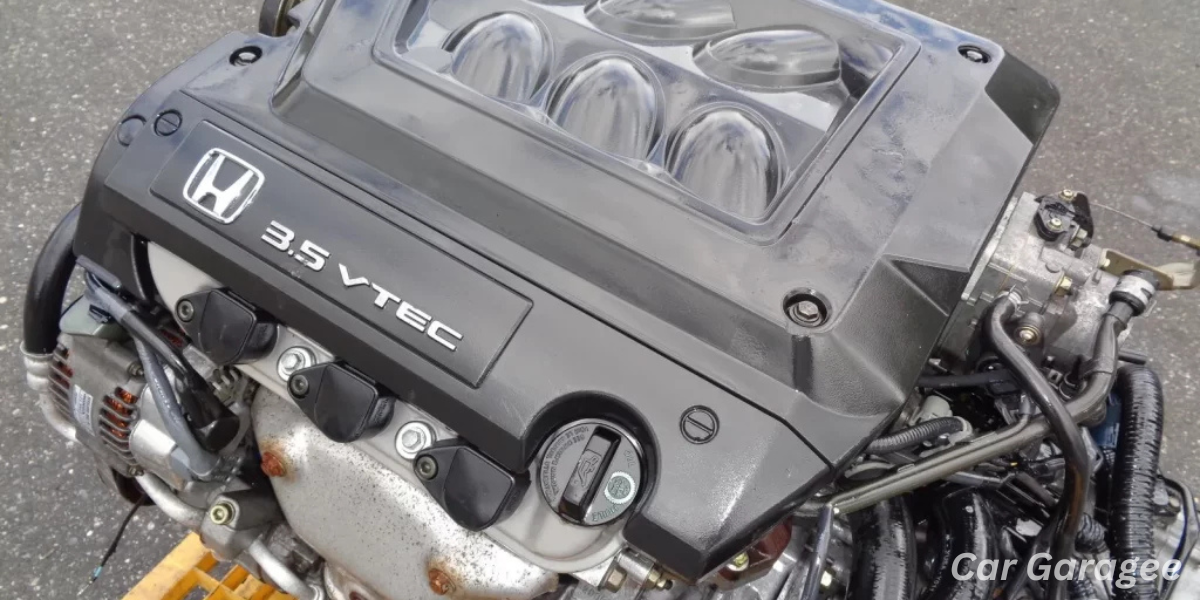
The Honda 3.5 V6 engine is engineered for exceptional reliability and consistent performance in the automotive world. This powertrain features six cylinders, strategically arranged in two banks to ensure smooth operation. The firing order is 1-4-2-5-3-6, a precise sequence designed to optimize power output while reducing wear and tear. In terms of layout, the front bank (near the passenger’s side) consists of cylinders 1, 3, and 5, while the rear driver’s side includes cylinders 2, 4, and 6.
This setup is standard in Honda models like the Odyssey, Pilot, Civic, and Accord ensuring high-quality driving experience. Supported by an aluminum-alloy block and robust cylinder heads, the 3.5L engine integrates VTEC technology for enhanced efficiency. A direct fuel injection system and optimized lubrication system provide a constant oil supply, maintaining performance and reducing engine wear. Additionally, the muffler configuration minimizes noise for a quiet and reliable drive.
What Causes Misfires in the Honda Odyssey?
The Honda Odyssey is known for its reliable engine performance, but like any vehicle, it can experience engine misfires, leading to noticeable issues such as loss of power, rough vibrations, and irregularities in the exhaust system.
Identifying the causes behind engine misfires is essential for ensuring optimal performance and long-term durability. Below are the key reasons for misfires in the Honda Odyssey and how to address them effectively.
1. Ignition System Issues:
One of the most common reasons for engine misfires in the Honda Odyssey is problems with the ignition system. Faulty spark plugs can become damaged or worn out, leading to weak sparks and poor combustion, which directly impacts engine performance. A malfunctioning ignition coil can also contribute to misfires, preventing the engine from firing correctly.
How to Fix It:
- Regularly inspect and replace spark plugs that show signs of wear.
- Check for any damaged ignition coils and replace them if needed.
- If the issue persists, seek professional assistance to avoid further engine damage.
2. Fuel System Problems:
The fuel system plays a vital role in delivering the correct fuel-air mixture for combustion. Over time, fuel injectors can become clogged or blocked, disrupting the fuel supply and leading to engine misfires. Insufficient fuel pressure caused by a failing fuel pump or a dirty fuel filter can also result in incomplete combustion, affecting the overall engine efficiency.
How to Fix It:
- Perform regular fuel system maintenance, including cleaning the fuel injectors.
- Ensure that the fuel pump and fuel filter are functioning properly.
- Monitor fuel pressure levels to maintain optimal combustion efficiency.
3. Air Intake Issues:
For the Honda Odyssey’s engine to operate efficiently, it requires the right air-fuel ratio. If unmetered air enters the engine due to air intake leaks, it can cause misfiring. A faulty Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor can also send incorrect readings to the engine control unit (ECU), negatively impacting fuel delivery and causing performance issues.
How to Fix It:
- Inspect the air intake system for leaks or cracks and seal them immediately.
- If the MAF sensor is providing inaccurate data, consider replacing it to restore proper fuel injection control.
4. Mechanical Issues:
Engine misfires can also stem from mechanical failures such as low cylinder compression, which can be caused by faulty valves, worn-out cylinder walls, or damaged piston rings. If a cylinder is unable to maintain the correct compression level, it will struggle to ignite the fuel-air mixture, leading to engine misfires and overall performance decline.
How to Fix It:
- Conduct a compression test to determine if a specific cylinder is underperforming.
- Replace worn-out engine components, including valves, piston rings, and cylinder walls, as needed.
- Address mechanical issues early to prevent costly engine repairs.
5. Timing Chain/Belt Issues:
The timing chain or timing belt ensures that the engine’s components are properly synchronized. If the timing belt slips or wears out, it can lead to misalignment between the pistons and valves, causing engine misfires. A worn timing chain tensioner can also contribute to irregular engine operation, affecting combustion efficiency.
How to Fix It:
- Regularly inspect the timing belt or timing chain for wear and tear.
- Replace the timing components as per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- If the issue persists, visit a Honda service center for expert diagnostics and repairs.
Read More:
How To Put Your 2020 Alfa Romeo In All-Wheel Drive?
Squealing Brakes at Low Speed: Causes & Solutions
Honda Odyssey Misfire Diagnosis
FAQS
What is the firing order of a 2013 Honda Accord 3.5 L?
The firing order of a 2013 Honda Accord 3.5 L V6 engine is 1-4-2-5-3-6. The cylinders are arranged with 1, 2, and 3 on the back side of the engine (from left to right) and 4, 5, and 6 on the front in the same direction. This sequence ensures smooth performance and efficient combustion across both banks.
What is the best firing order for a V6?
The firing orders of V6 engines depend on the angle between the cylinder banks. A 90-degree V6 can use R1-L2-R2-L3-L1-R3 or R1-L3-R3-L2-R2-L1, while a 60-degree V6 often follows R1-L1-R2-L2-R3-L3. In flat-six engines, common patterns include R1-L2-R3-L1-R2-L3 and R1-L3-R2-L1-R3-L2. The right firing order ensures smooth operation and reduces engine stress.
How does the 3.5 L Power Boost work?
The Ford Power Boost pairs a twin-turbocharged 3.5-liter V-6 engine with a 1.5-kWh lithium-ion battery and a 47-horsepower motor, creating a strong hybrid powertrain. This setup, available in the new Ford F-150, delivers a jaw-dropping 430 horsepower and 570 pound-feet of torque. It enhances fuel efficiency, helping drivers save at the pump while maintaining impressive performance.
What is the ideal firing order?
The standard 1-3-4-2 firing order is widely used due to its optimal balance and smooth power delivery. It improves overall engine performance and efficiency. Some alternative firing orders, such as 1-2-4-3 and 1-4-3-2, can cause increased vibrations, uneven power output, and reduced thermal and fuel efficiency.
Why is a 6-cylinder engine better than a 4-cylinder?
A V6 engine delivers higher torque output than a four-cylinder engine, allowing for smoother performance, especially under load. A six-cylinder engine can usually out-tow a four-cylinder, making it a better option for hauling, towing, and high-performance driving. Its power delivery ensures improved acceleration and efficiency, making it a handy choice for drivers who need extra strength on the road.
How many pistons does a V6 have?
A V6 engine contains 6 pistons, while a 4-cylinder engine has 4 pistons. When gas combusts, it pushes the pistons, transferring power to the crankshaft. More cylinders mean more power generation, improving overall engine performance. Each piston connects to ensure a balanced and efficient combustion cycle, which enhances speed and responsiveness in a vehicle.

Mian Hashir is a passionate automotive enthusiast and the lead author at Car Garagee, a website dedicated to providing in-depth car reviews, maintenance tips, and the latest news in the automotive world. With years of experience in the industry, Hashir combines his technical knowledge with a love for cars to deliver insightful and engaging content. Whether you’re a car owner or a curious reader, Mian Hashir’s articles help readers make informed decisions, from choosing the right vehicle to understanding how to keep it in top condition.